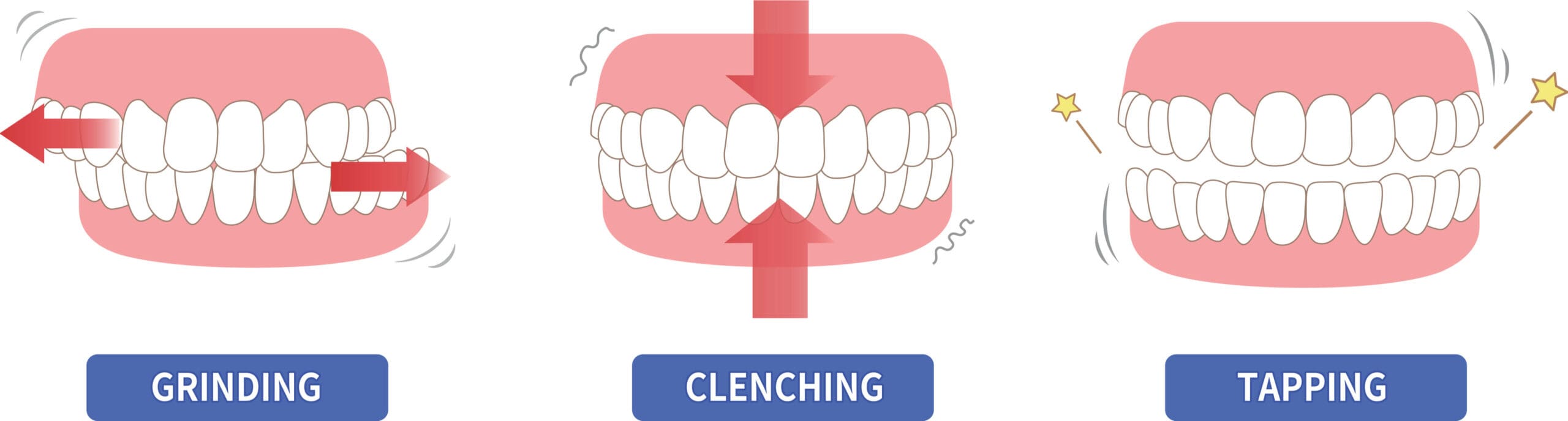
What is Bruxism:
Bruxism is the medical term for unconscious teeth clenching and grinding, either while awake or asleep. Patients with bruxism can experience headache, earaches, facial pain, and even migraines. Bruxism damages the teeth leading to increased tooth sensitivity, flattening, chipping or fracture of the teeth and jaw joint (TMJ) problems. Patients who grind their teeth while asleep often wake up with a sore jaw. Chronic clenching can lead to hypertrophy of the masseter muscle (the muscle responsible for eating and clenching), giving the appearance of a wide face or square jaw.
Treatment Options for Bruxism:
Botox (Botulinum Toxin Type A)
Treatment of bruxism involves using dental devices such as a “nightguard” or bite block to prevent the teeth from contacting one another. These dental devices help prevent damage to the teeth but do not change the fact that patients are still physically clenching and grinding. In order to decrease the clenching, grinding and reduce the biting force exerted on the teeth, we have recently started using Botox (Botulinum Toxin Type A) to decrease the excessive muscle activity of the jaw. Botox treatment can provide pain relief and help prevent dental problems related to bruxism. It can also soften the appearance of the jaw line, help prevent damage to the TMJ (temporomandibular joint) and decrease TMJ associated headaches.
The masseter muscle is injected with a small volume of Botox to decrease the overactivity of the muscle. This helps to normalize the clenching force of the jaw and relieve the bruxism. The effect of Botox lasts for approximately three to four months, after which the procedure can be repeated. Patients are often advised to continue use of their night guard, and both of these measures can provide effective relief.
